
Abstract of Raw Materials for Organic Fertilizers
Organic fertilizers are widely used in different countries, and their choice of raw materials for production varies according toagricultural and resource characteristics. Each country has the opportunity to choose the right feedstock for organic fertilizerproduction according to its needs, while at the same time achieving efficient use of waste.
1) In countries with more adequate agricultural development, such as the United States and Canada, there is a tendency touse agricultural wastes as raw materials for organic fertilizer production. Crop residues, grain hulls, vegetable peels andlivestock manure are widely collected and processed to make efficient organic fertilizers. This method not only reduces theburden of agricultural waste disposal, but also converts it into organic resources that can be provided to farmland as nutrientsupplements.
2) In contrast, some resource-poor countries choose to use municipal waste and household garbage as raw materials fororganic fertilizer production. This practice not only effectively reduces the accumulation of urban waste, but also converts itinto organic fertilizers that can be provided to farmland around the city. Through scientific treatment and separationtechnology, the useful components in organic waste can be extracted, and even anaerobic digestion can be carried out toproduce biogas for energy recycling.
3) Some countries with developing agriculture, such as China and India, choose to use local agricultural resources in theproduction of organic fertilizers. These countries have vast areas of farmland and a wide variety of crops. When producingorganic fertilizers, they focus on local crop residues such as rice straw and straw as the main raw materials for organicfertilizer production. Through effective treatment and fermentation, these crop residues can be transformed into highlyefficient organic fertilizers, which can be used for fertilizing farmland and soil improvement to improve crop yield and quality.
In general, raw materials for organic fertilizer production vary from country to country, but all are committed to the efficientuse of waste and the sustainability of agricultural development. This flexibility in the choice of raw materials for productionallows different countries to develop their own organic fertilizer production programs based on their own characteristics and resources, contributing to healthy agricultural development and recycling of waste.

Example :
) Senegal: In Senegal, the most commonly used feedstock for organic fertilizer is animal manure, especially poultry manure.This is because Senegalese agriculture relies on poultry farming, which consists mainly of poultry, cattle and sheep.
2) Kenya: In Kenya, a common organic fertilizer feedstock is cattle manure. Kenya has a large number of family farms andcattle farms, making cow dung an easily available and effective raw material for organic fertilizer.
3) Nigeria: Nigeria is one of the largest oil palm growing countries in Africa, and oil palm residue is one of the important rawmaterials for organic fertilizer production in Nigeria. This plant waste is rich in nutrients and can be used to make highlyeffective organic fertilizer.
4) Madagascar: Madagascar is an island country surrounded by rich marine resources. Therefore, Madagascar uses seaweedas a raw material for organic fertilizers and this plant is rich in micronutrients and plant growth factors.
5) Ethiopia: Ethiopia’s agriculture is based on crop rotation between farmlands and raising livestock. Therefore, commonorganic fertilizer feedstocks used in Ethiopia are mixtures of animal and plant wastes such as animal manure, straw and ricehusks.
Each country has its own unique environmental and agricultural characteristics and therefore the choice of raw materials fororganic fertilizers will vary.
A example of our organic fertilizer program :
In our organic fertilizer production line customers, there is a customer has a palm tree planting base and palm oil productionplant, because of the industry, every year will produce a large number of palm fruit waste, he found us, intends to set up apalm fiber as the raw material for organic fertilizer production line, the production of organic fertilizer can not only be put into use with the planting of palm trees, and even can be sold to the outside world, not only reduces the annual purchase of notonly reduce the cost of purchasing fertilizer every year, but also bring him more profit, realize the cycle of production andreduce pollution.
After a detailed discussion, we reached a cooperation with the customer, designed the organic fertilizer production lineprogram suitable for local raw materials and resource conditions, and quickly put into production and use, to achieve a win-win situation!

Selection of Organic Fertilizer Raw Materials in Different Regions :
- Southeast Asia (Indonesia, Malaysia, Philippines, etc.) :
Indonesia is one of the world’s largest producers and exporters of palm oil. The country’s palm oil industry plays an importantrole in its economy, contributing to employment, foreign exchange earnings and economic growth. However, the industry isalso associated with various environmental and social issues.
Growing global demand for palm oil has fueled the expansion of palm plantations in Indonesia, which is used in a variety ofproducts, including food, cosmetics, and biofuels. The country has large tracts of land suitable for palm cultivation,particularly on the islands of Sumatra and Kalimantan (Borneo), which have become major palm oil producing areas.
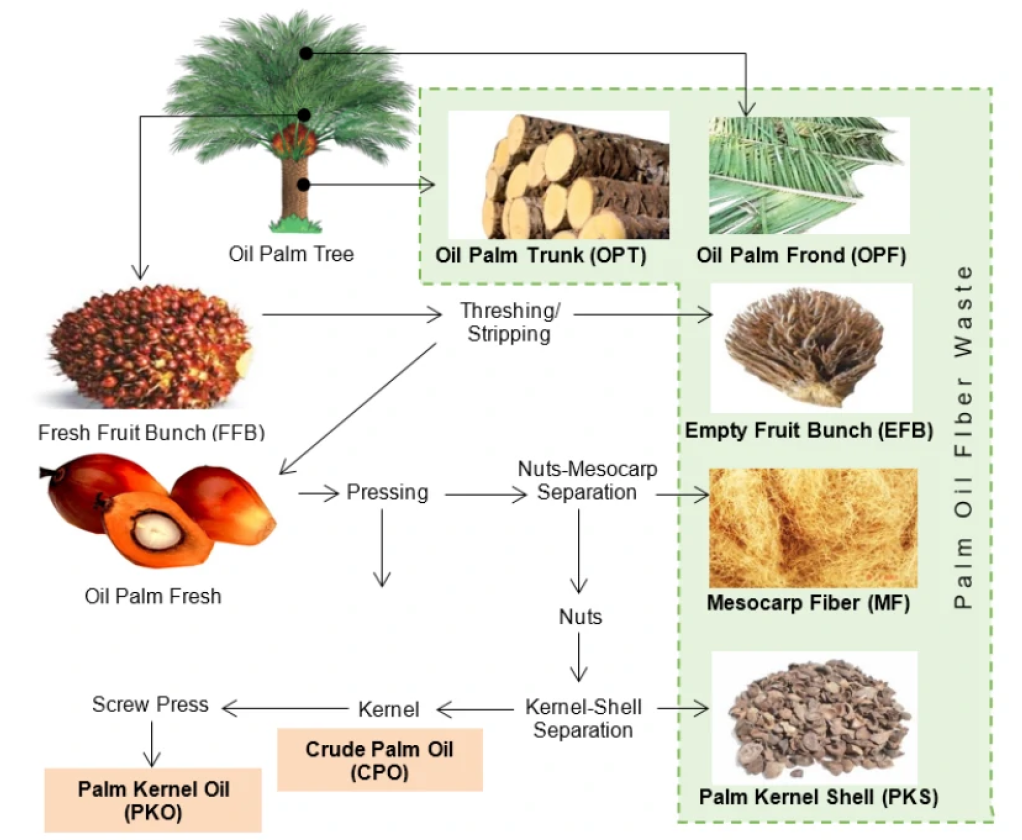
Palm oil production is important to Indonesia’s economy as the country is the world’s largest producer and consumer of thecommodity, providing about half of the world’s supply.In 2016, Indonesia produced more than 34.6 million tons of palm oiland exported 25.1 million tons. Oil palm plantations cover at least 12 million hectares (30 million acres).
The average annual growth rate of palm oil plantation area reached 10.31% between 1970-2017. However, a dramaticallygrowing industry can also lead to more serious environmental waste problems. The only palm oil derivative commoditiestraded globally are CPO (crude palm oil) and PKO (palm kernel oil). These two products account for only 30% of the palm oiltree. The remaining 70% will be unutilized. The remaining 70% will be unutilized biomass waste. In addition, 10% of thepalm oil waste is reused, while the rest becomes residue, causing serious environmental problems.
Palm oil residue itself is rich in nutrients and is suitable as a raw material for organic fertilizers. It contains high levels oforganic matter, nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium and other nutrients, as well as fatty acids and micronutrients, which providea comprehensive supply of nutrients to plants. Proper treatment and fermentation of palm oil waste residue can improve itsnutrient utilization and make it an effective organic fertilizer.
Furthermore, the utilization of palm oil waste residue promotes a circular economy in the agricultural system. Throughprocesses such as enzyme treatment and mixed fermentation, palm oil waste residue can be converted into organic veggiesand organic fertilizers, which provide nutrient supplementation to farmland. At the same time, organic fertilizer plays apositive role in the increase and improvement of soil organic matter, improves the soil’s ability to retain water and fertilizer,and strengthens the ability of crops to resist disease and drought.
In addition, the use of palm oil waste residue also helps to reduce the use of chemical fertilizers. Organic fertilizers canprovide comprehensive nutrients needed by plants and improve soil structure, thus reducing dependence on chemical fertilizers, reducing the use of chemical fertilizers in agriculture, and lowering the load on the environment and the productioncosts of agriculture.
In summary, the production of organic fertilizers using palm oil waste residue, which is abundant in Indonesia, has manyadvantages. Not only can it effectively reduce the burden of waste residue disposal, but it can also be transformed into auseful agricultural resource that provides the comprehensive nutrition required by plants and improves soil quality, thusrealizing the sustainable development of agriculture.

- Latin America (Ecuador, Mexico, etc.)
The increase in food waste generation and its management is a major problem. In the European Union, about 100 milliontons of food are wasted every year, mainly from households but also from food markets. This is expected to increase to morethan 120 million tons by 2020 if the situation does not change.
In developing countries, the situation is even worse. The main food waste streams originate from food marketactivities/regions, which are often highly productive and inefficient in waste management. In addition, these food wastestreams are often included in total municipal solid waste generation.
It has been reported that food market waste accounts for 9% of total municipal solid waste generation in Guadalajara, Mexico.
These organic wastes, especially food market wastes, are disposed of in landfills or dumps along with municipal solid wastes,which can have different adverse and negative impacts on the environment (bad odors, leachate generation and emission ofgreenhouse gases into the atmosphere, among others), affecting the health of the populations in the area of influence.
Therefore, the timely disposal of these wastes has become a matter of urgency. The high concentration of organic matter andnutrients in food market and urban horticultural wastes facilitates their recovery through composting, which makes it possibleto manage and recycle these materials to obtain a final product (organic fertilizer) for agricultural purposes.
Composting is defined as the biological decomposition of organic matter under controlled aerobic conditions to form a stable,humus-like end product. Among the major waste management strategies developed, composting is receiving increasingattention in organic waste treatment as a more economically and environmentally profitable treatment method, resulting in astabilized end product.
On the one hand, from an economic point of view, compost can be distributed in a wide variety of markets, especially whenthe demand for fertilizers is closely linked to high agricultural prices. On the other hand, at the environmental level,composting not only avoids landfills and reduces the formation of leachate and gases, but also implies the acquisition of afinished product that can fertilize the soil and contribute to water savings.
In this sense, composting is an easier and less expensive technology to implement than other technological options. However,while composting can be a viable alternative for managing such waste streams, there is currently insufficient information onthe composting of food market and pruning wastes in developing countries and on the added value of the compost obtained.
As a manufacturer of fertilizer production lines with decades of experience, we are a leader in the fertilizer industry with awealth of solutions, strong technical support, and one-stop customer service to provide counterpart support.
- Australia, North America
Australia and North America, as countries with rich wildlife resources and agricultural industries, produce a considerableamount of animal waste every year. These wastes mainly come from abattoirs, farms, breeding farms and other places.
There are over 120,000 rural enterprises in Australia with a mix of production systems that provide greenhouse gas sources.Effluent from pig farms, cattle feedlots and dairy farms appear to offer immediate potential to harvest methane to producebiogas for electricity generation. Feedlots currently generate over 10 million tonnes of manure every year.
Some of the common animal wastes include animal carcasses, feces, waste from sheep shearing etc. These wastes need tobe properly treated and disposed of to prevent negative impacts on the environment and public health.
Animal waste is rich in organic matter and nutrients
Organic materials in animal waste include feces, urine and plant residues, which are rich in elements such as carbon,hydrogen and oxygen, and can provide essential nutrients for plants after decomposition.
In addition, animal waste is also rich in nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium and other micronutrients needed for plant growth. These nutrients can meet the needs of crop growth and development, and help improve soil quality and increase crop yields.
If animal wastes are not properly disposed of, they may cause environmental pollution and waste of resources. Accumulationof waste may lead to contamination of soil and water sources, air hazards from the emission of large quantities of gases suchas methane, and potential health risks. Proper utilization of animal waste can effectively reduce these risks.
By converting waste into organic fertilizers, the negative impacts of waste on the environment can be reduced and it can helpto improve the structure and quality of the soil. The use of organic fertilizers also reduces the need for synthetic fertilizers, which in turn reduces the negative impacts of chemical fertilizer manufacturing processes, such as energy consumption andgreenhouse gas emissions.
Animal waste also has good renewable properties. Animal waste generated in agriculture is a renewable resource that can becollected and treated as needed. Animal wastes can be converted into organic fertilizers through appropriate treatmentmethods such as composting, anaerobic fermentation or biogasification. The waste conversion process can effectively reducethe volume of waste while improving the quality and availability of fertilizer.
To fully utilize animal wastes as raw materials for organic fertilizers, appropriate handling and management measures mustbe taken. These include collection, storage and disposal of waste, as well as proper fertilization and management ofagricultural land. It is also necessary to comply with relevant laws and regulations and environmental protection guidelines toensure that the waste is handled safely and in an environmentally friendly manner.
By making full use of animal waste, it is possible to achieve sustainable agriculture, improve soil quality, increase crop yieldsand reduce dependence on chemical fertilizers, thus unifying the economic, environmental and social benefits of agricultural production.

- Middle East, e.g. Egypt, Saudi Arabia, etc.
The amount of agricultural waste in Egypt ranges from 300-35 million tons per year, of which only 7 million tons are used asanimal feed and 4 million tons as organic fertilizers.
These crop residues are leaves, stems and racks produced after harvesting on farms and are characterized by coarse plantby-products, large in size and chemically low in protein and fat. It is also high in lignin and cellulose.
The problem of agricultural wastes becomes very visible and aggregated after the harvesting of summer crops. This isbecause during this season the farmer is anxious to re-cultivate the land and hence disposal of the waste is his first priority,usually by burning. This method of burning not only causes economic losses but also has harmful effects on the environment.These harmful effects are emission of toxic gases into the air and reduction of microbial activity in the soil.
In addition, compacting and storing these wastes in the field may provide a suitable environment for the reproduction andgrowth of pests and pathogens that attack new crops. Therefore, it is important to utilize agricultural wastes in any otherenvironmentally friendly way.
These can be done in the following ways:
1) Producing compost through fermentation agriculture, the main way is recycling agriculture. This will help to fertilize the soilorganically and reduce the cost of production.
2) Animal feed production:- By treating some wastes like rice straw with urea or ammonia in order to increase its nitrogencontent and hence its nutritional value.
In 2021, only about 4.3 million tons of crop residues out of 25 million tons produced were used in feeding. Approximately twothird of the crop residues were burned or wasted.
There were attempts to upgrading the nutritive value of the crop residues through mechanical, chemical and biologicaltreatment. The treatment of crop residues takes place at farm level, however there are opportunities for biological treatmentsto produce green crop residues that can be used as organic fertilizers or silage.
Utilization of agriculture waste in an environmentally friendly way is very important, and is a market opportunity for privatesector. Across the value chain from collection, transportation to production.
Water resources are very limited in the Middle East, and therefore the development of agriculture is severely restricted. Theuse of agricultural wastes as organic fertilizers improves the water retention properties of the soil, reduces water loss andwastage, provides better water use efficiency during crop growth, and improves the nutrient availability of the soil to promotecrop growth and increased yields.
By choosing to use agricultural waste as the raw material for organic fertilizer production, Middle Eastern countries are ableto make full use of waste resources, increase soil fertility, protect the environment and promote sustainable agriculturaldevelopment. This is important for agricultural economic development, soil protection and environmental sustainability in theMiddle East.

